回调和反应式编程都可以实现系统吞吐量有效提升,但是这两种编程模式存在阅读、编写、调试困难的问题,所以实际项目中还是以线程池为主。但是 java 的线程是平台线程,可以理解为并行线程数最多等于 CPU 核数 (macOS 查看核数sysctl hw.physicalcpu hw.logicalcpu),并且存在线程内存占用大,上下文切换耗时高问题,所以在高并发请求中表现不如前面两种模式(spring reactive 和 vertx 模式并没有流行起来)。
JEP 444: Virtual Threads 主要目标在优化 IO 密集型任务时创建平台线程会消耗过多内存以及线程上下文切换耗时问题。
虚拟线程的优势:1. 和线程 API 兼容(大部分兼容)2. 降低应用内存使用,提升系统可用性,减少内存不足异常 OutOfMemoryError: unable to create new native thread 3. 提升代码可读性(相比 reactive 编程)。
本文是 VirtualThread 快速笔记,包含 API 使用、限制和在 Spring Boot 的实际使用以及与 Kotlin 协程的对比。
VirtualThread API
创建虚拟线程有以下方法
// 1
Runnable task = () -> { System.out.println("Hello Virtual Thread!"); };
Thread.startVirtualThread(task);
// 2
Thread vThread = Thread.ofVirtual().start(task);
// 3
Thread vThread = Thread.ofVirtual().unstarted(task);
vThread.start();
// 4
Executor vExecutor = Executors.newVirtualThreadPerTaskExecutor();
vExecutor.execute(task); // unlimited virtual threads
// 5 newThreadPerTaskExecutor but with VirtualThreadFactory
ThreadFactory vThreadFactory = Thread.ofVirtual().name("vt-", 1).factory();
Executor vExecutor = Executors.newThreadPerTaskExecutor(vThreadFactory);
vExecutor.execute(task);
虚拟线程相比平台线程,在创建耗时和内存占用具有很大优势。作为对比,同一台机器上创建 1W 个平台线程和虚拟线程。
| 类型 | 创建时间 | 内存占用 |
|---|---|---|
| virtual thread | 91 ms | 4.4mb |
| platform thread | 998 ms | 14.3gb |
limitations of VirtualThread
下面说的 carrier thread 就是执行虚拟线程的系统线程(platform thread)。
Avoid synchronized blocks/methods, use
ReentrantLock.Object monitor = new Object(); //... public void aMethodThatPinTheCarrierThread() throws Exception { // The virtual thread cannot be unmounted because it holds a lock, // so the carrier thread is blocked. // also called pinned thread or pinning synchronized(monitor) { Thread.sleep(1000); } }Avoid monopolization. 即避免 CPU 密集型的任务使用虚拟线程。如果一个 task 耗时非常长,那么该虚拟线程对应的 platform thread(即 the carrier thread)无法让出去执行其他任务,JVM 会创建新的线程。这种场景应该使用线程池技术。
Cation the carrier thread pool elasticity. 当前发生 1 或者 2 的情况时,JVM 会创建新的系统线程,容易导致系统内存被耗尽。
Avoid Object pooling, or reduce
ThreadLocalUsage: 因为线程池数量有限制且线程会复用,所以创建比较耗时的对象会被池化以复用。但是虚拟线程不满足线程的这两个假设,池化对象并不能被复用。更糟糕的是,由于虚拟线程个数一般没有限制,每个虚拟线程都有 ThreadLocal 对象的话,可能耗尽 JVM 堆内存。JEP 429: Scoped Values will fix this.关注线程安全,虚拟线程本质还是多线程编程,和多线程一样需要关注共享状态问题。
use VirtualThread in Spring Boot
@SpringBootApplication
@Slf4j
public class VirtualthreadApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(VirtualthreadApplication.class, args);
}
@Bean
public TomcatProtocolHandlerCustomizer<?> protocolHandlerVirtualThreadExecutorCustomizer() {
return protocolHandler -> {
log.info("Configuring " + protocolHandler + " to use VirtualThreadPerTaskExecutor");
protocolHandler.setExecutor(Executors.newVirtualThreadPerTaskExecutor());
};
}
}
use VirtualThread in Quarkus
Using virtual threads in Quarkus is straightforward. You only need to use the @RunOnVirtualThread annotation. It indicates to Quarkus to invoke the annotated method on a virtual thread instead of a regular platform thread.
@Path("/greetings")
public class VirtualThreadApp {
@RestClient RemoteService service;
@GET
@RunOnVirtualThread
public String process() {
// Runs on a virtual thread because the
// method uses the @RunOnVirtualThread annotation.
// `service` is a rest client, it executes an I/O operation
var response = service.greetings(); // Blocking, but this time, it
// does neither block the carrier thread
// nor the OS thread.
// Only the virtual thread is blocked.
return response.toUpperCase();
}
}
When Quarkus meets Virtual Threads)
internal and compare to kotlin coroutine
A coroutine is an instance of suspendable computation. - Kotlin doc
和 kotlin 的协程类似,java 的虚拟线程同样不能自己执行,而是需要挂载到平台线程上面才能执行。下面是虚拟线程的生命周期:
/*
* Virtual thread state and transitions:
*
* NEW -> STARTED // Thread.start
* STARTED -> TERMINATED // failed to start
* STARTED -> RUNNING // first run
*
* RUNNING -> PARKING // Thread attempts to park
* PARKING -> PARKED // cont.yield successful, thread is parked
* PARKING -> PINNED // cont.yield failed, thread is pinned
*
* PARKED -> RUNNABLE // unpark or interrupted
* PINNED -> RUNNABLE // unpark or interrupted
*
* RUNNABLE -> RUNNING // continue execution
*
* RUNNING -> YIELDING // Thread.yield
* YIELDING -> RUNNABLE // yield successful
* YIELDING -> RUNNING // yield failed
*
* RUNNING -> TERMINATED // done
*/
private static final int NEW = 0;
private static final int STARTED = 1;
private static final int RUNNABLE = 2; // runnable-unmounted
private static final int RUNNING = 3; // runnable-mounted
private static final int PARKING = 4;
private static final int PARKED = 5; // unmounted
private static final int PINNED = 6; // mounted
private static final int YIELDING = 7; // Thread.yield
private static final int TERMINATED = 99; // final state
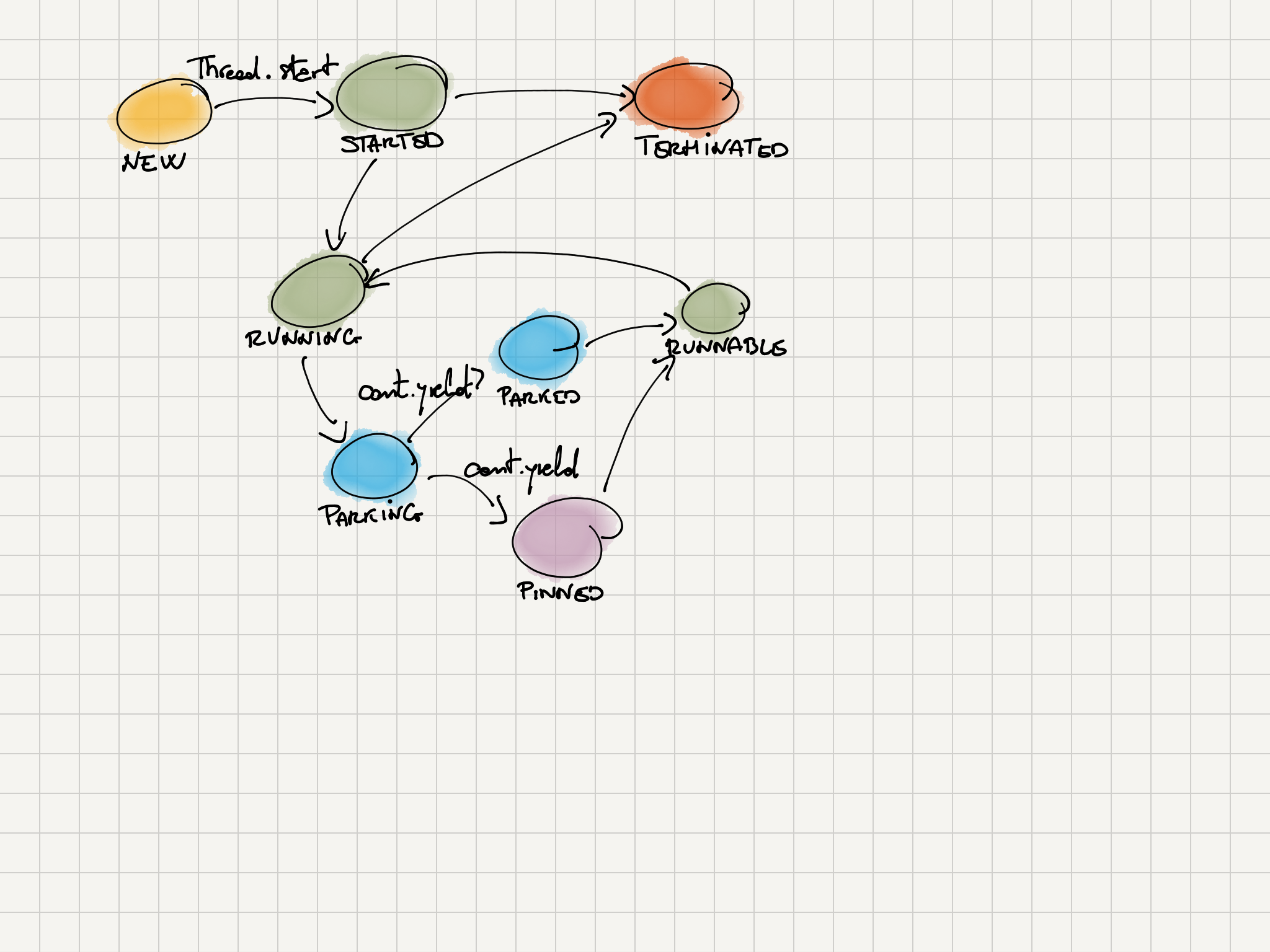
绿色表示虚拟线程挂载(mounted)在 平台线程(carrier thread)。蓝色表示 unmounted 并让出线程(去执行其他虚拟线程或者任务)。紫色表示 pinned。
核心代码解读参考Some Virtual Threads InternalsPermalink
参考
Why are Thread.stop, Thread.suspend and Thread.resume Deprecated?